Hinweis
Zum Ende gehen, um den vollständigen Beispielcode herunterzuladen oder dieses Beispiel über JupyterLite oder Binder in Ihrem Browser auszuführen.
Themenextraktion mit Non-negative Matrix Factorization und Latent Dirichlet Allocation#
Dies ist ein Beispiel für die Anwendung von NMF und LatentDirichletAllocation auf einen Korpus von Dokumenten und die Extraktion additiver Modelle der Themenstruktur des Korpus. Die Ausgabe ist eine Darstellung der Themen als Balkendiagramm, das die Top-Wörter basierend auf ihren Gewichten zeigt.
Non-negative Matrix Factorization wird mit zwei verschiedenen Zielfunktionen angewendet: der Frobenius-Norm und der verallgemeinerten Kullback-Leibler-Divergenz. Letztere ist äquivalent zu Probabilistic Latent Semantic Indexing.
Die Standardparameter (n_samples / n_features / n_components) sollten das Beispiel in wenigen zehn Sekunden ausführbar machen. Sie können versuchen, die Dimensionen des Problems zu erhöhen, aber beachten Sie, dass die Zeitkomplexität bei NMF polynomial ist. Bei LDA ist die Zeitkomplexität proportional zu (n_samples * iterations).
Loading dataset...
done in 1.066s.
Extracting tf-idf features for NMF...
done in 0.216s.
Extracting tf features for LDA...
done in 0.215s.
Fitting the NMF model (Frobenius norm) with tf-idf features, n_samples=2000 and n_features=1000...
done in 0.070s.
Fitting the NMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler divergence) with tf-idf features, n_samples=2000 and n_features=1000...
done in 1.396s.
Fitting the MiniBatchNMF model (Frobenius norm) with tf-idf features, n_samples=2000 and n_features=1000, batch_size=128...
done in 0.071s.
Fitting the MiniBatchNMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler divergence) with tf-idf features, n_samples=2000 and n_features=1000, batch_size=128...
done in 0.208s.
Fitting LDA models with tf features, n_samples=2000 and n_features=1000...
done in 2.313s.
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
from time import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
from sklearn.decomposition import NMF, LatentDirichletAllocation, MiniBatchNMF
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfVectorizer
n_samples = 2000
n_features = 1000
n_components = 10
n_top_words = 20
batch_size = 128
init = "nndsvda"
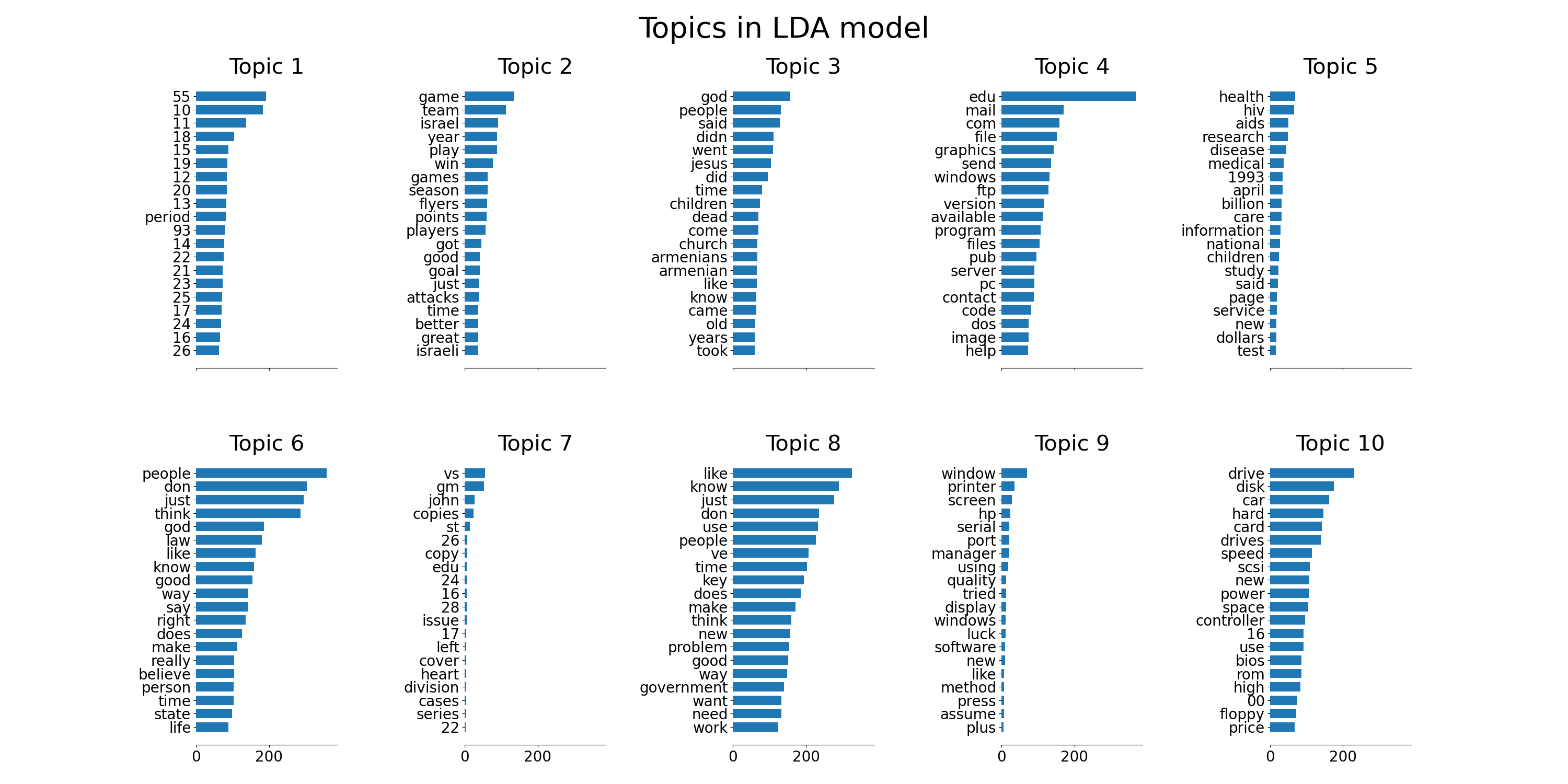
def plot_top_words(model, feature_names, n_top_words, title):
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 5, figsize=(30, 15), sharex=True)
axes = axes.flatten()
for topic_idx, topic in enumerate(model.components_):
top_features_ind = topic.argsort()[-n_top_words:]
top_features = feature_names[top_features_ind]
weights = topic[top_features_ind]
ax = axes[topic_idx]
ax.barh(top_features, weights, height=0.7)
ax.set_title(f"Topic {topic_idx + 1}", fontdict={"fontsize": 30})
ax.tick_params(axis="both", which="major", labelsize=20)
for i in "top right left".split():
ax.spines[i].set_visible(False)
fig.suptitle(title, fontsize=40)
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.90, bottom=0.05, wspace=0.90, hspace=0.3)
plt.show()
# Load the 20 newsgroups dataset and vectorize it. We use a few heuristics
# to filter out useless terms early on: the posts are stripped of headers,
# footers and quoted replies, and common English words, words occurring in
# only one document or in at least 95% of the documents are removed.
print("Loading dataset...")
t0 = time()
data, _ = fetch_20newsgroups(
shuffle=True,
random_state=1,
remove=("headers", "footers", "quotes"),
return_X_y=True,
)
data_samples = data[:n_samples]
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
# Use tf-idf features for NMF.
print("Extracting tf-idf features for NMF...")
tfidf_vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(
max_df=0.95, min_df=2, max_features=n_features, stop_words="english"
)
t0 = time()
tfidf = tfidf_vectorizer.fit_transform(data_samples)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
# Use tf (raw term count) features for LDA.
print("Extracting tf features for LDA...")
tf_vectorizer = CountVectorizer(
max_df=0.95, min_df=2, max_features=n_features, stop_words="english"
)
t0 = time()
tf = tf_vectorizer.fit_transform(data_samples)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
print()
# Fit the NMF model
print(
"Fitting the NMF model (Frobenius norm) with tf-idf features, "
"n_samples=%d and n_features=%d..." % (n_samples, n_features)
)
t0 = time()
nmf = NMF(
n_components=n_components,
random_state=1,
init=init,
beta_loss="frobenius",
alpha_W=0.00005,
alpha_H=0.00005,
l1_ratio=1,
).fit(tfidf)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
tfidf_feature_names = tfidf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
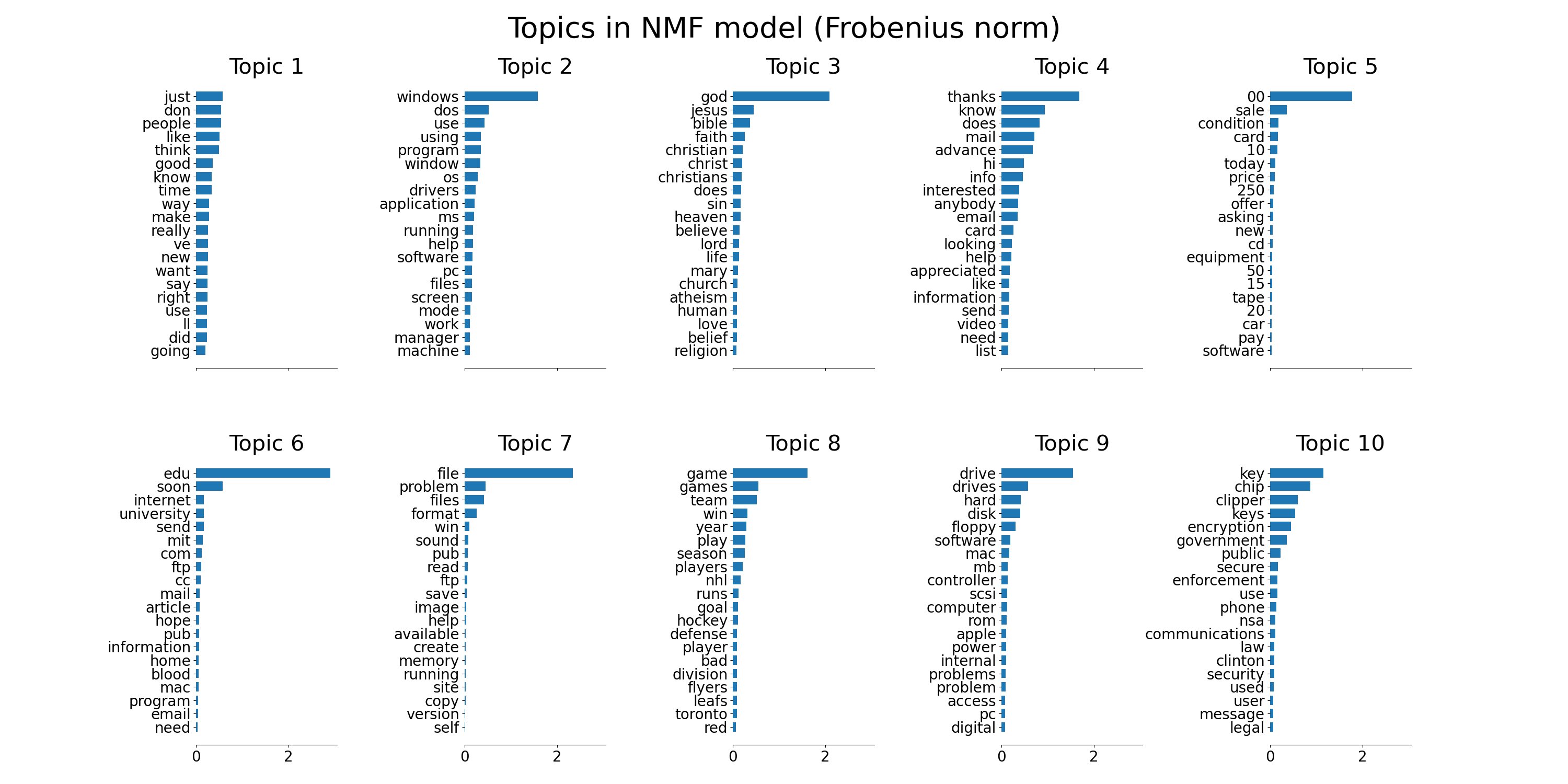
plot_top_words(
nmf, tfidf_feature_names, n_top_words, "Topics in NMF model (Frobenius norm)"
)
# Fit the NMF model
print(
"\n" * 2,
"Fitting the NMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler "
"divergence) with tf-idf features, n_samples=%d and n_features=%d..."
% (n_samples, n_features),
)
t0 = time()
nmf = NMF(
n_components=n_components,
random_state=1,
init=init,
beta_loss="kullback-leibler",
solver="mu",
max_iter=1000,
alpha_W=0.00005,
alpha_H=0.00005,
l1_ratio=0.5,
).fit(tfidf)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
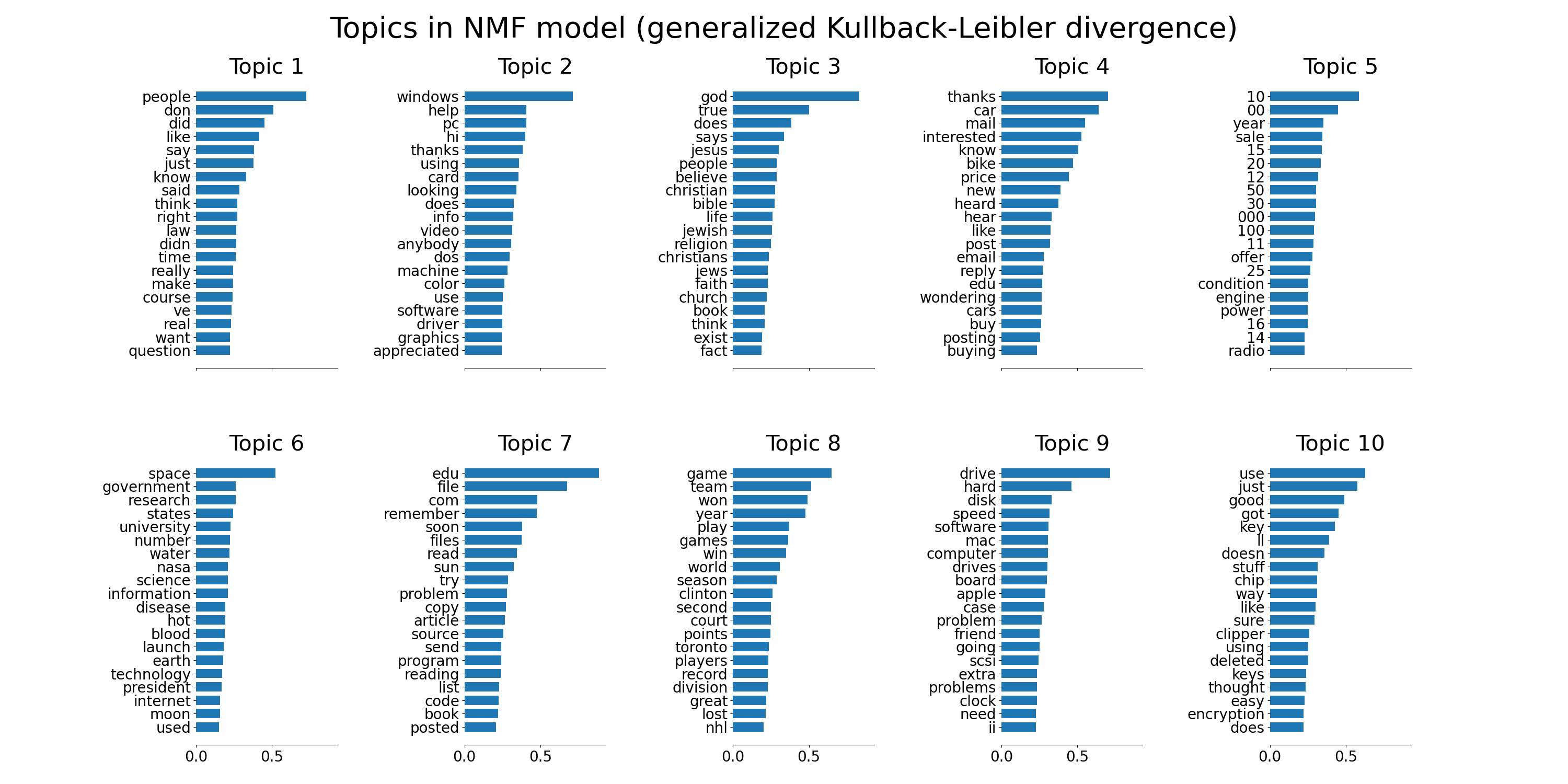
tfidf_feature_names = tfidf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
plot_top_words(
nmf,
tfidf_feature_names,
n_top_words,
"Topics in NMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler divergence)",
)
# Fit the MiniBatchNMF model
print(
"\n" * 2,
"Fitting the MiniBatchNMF model (Frobenius norm) with tf-idf "
"features, n_samples=%d and n_features=%d, batch_size=%d..."
% (n_samples, n_features, batch_size),
)
t0 = time()
mbnmf = MiniBatchNMF(
n_components=n_components,
random_state=1,
batch_size=batch_size,
init=init,
beta_loss="frobenius",
alpha_W=0.00005,
alpha_H=0.00005,
l1_ratio=0.5,
).fit(tfidf)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
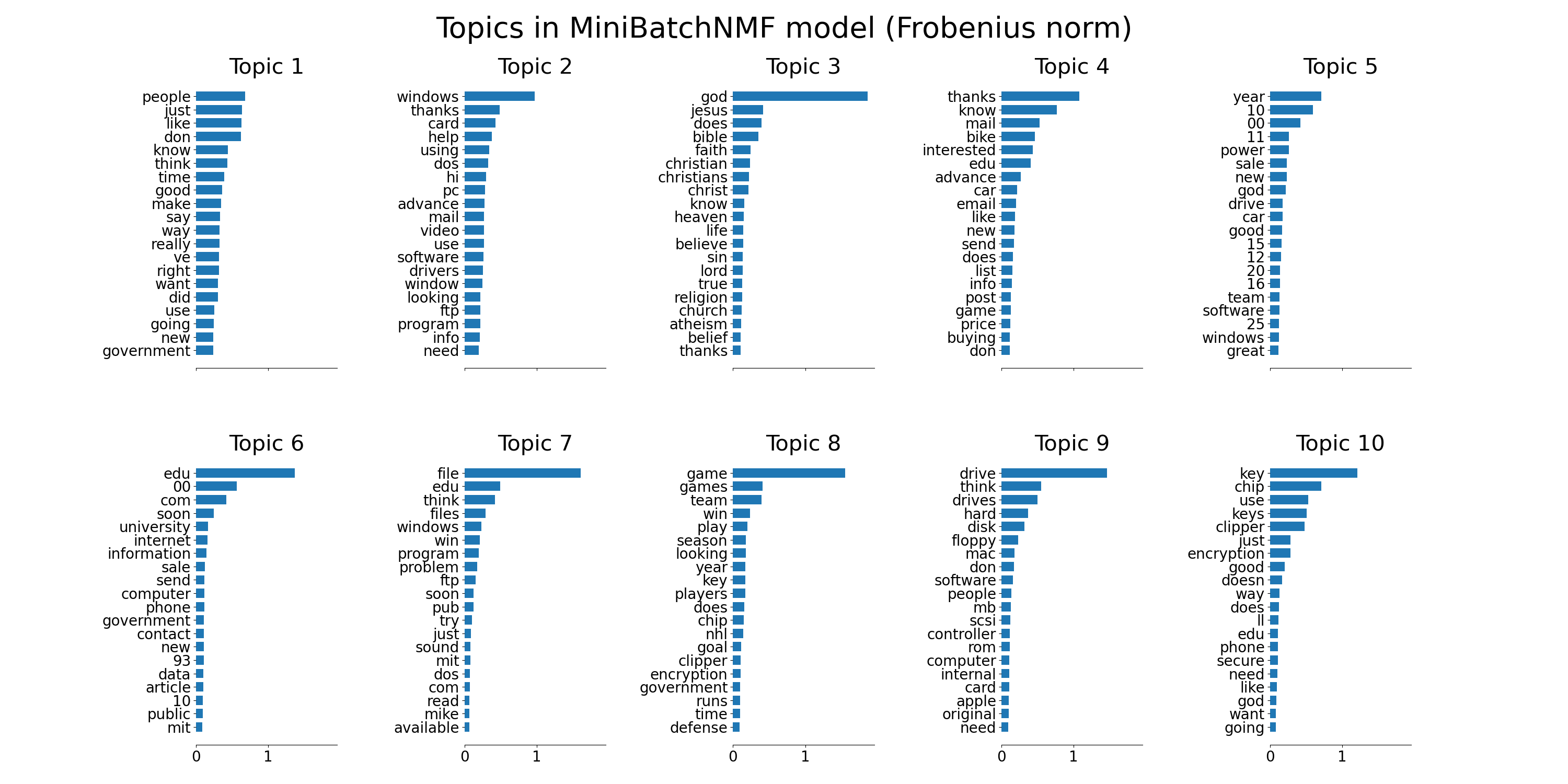
tfidf_feature_names = tfidf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
plot_top_words(
mbnmf,
tfidf_feature_names,
n_top_words,
"Topics in MiniBatchNMF model (Frobenius norm)",
)
# Fit the MiniBatchNMF model
print(
"\n" * 2,
"Fitting the MiniBatchNMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler "
"divergence) with tf-idf features, n_samples=%d and n_features=%d, "
"batch_size=%d..." % (n_samples, n_features, batch_size),
)
t0 = time()
mbnmf = MiniBatchNMF(
n_components=n_components,
random_state=1,
batch_size=batch_size,
init=init,
beta_loss="kullback-leibler",
alpha_W=0.00005,
alpha_H=0.00005,
l1_ratio=0.5,
).fit(tfidf)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
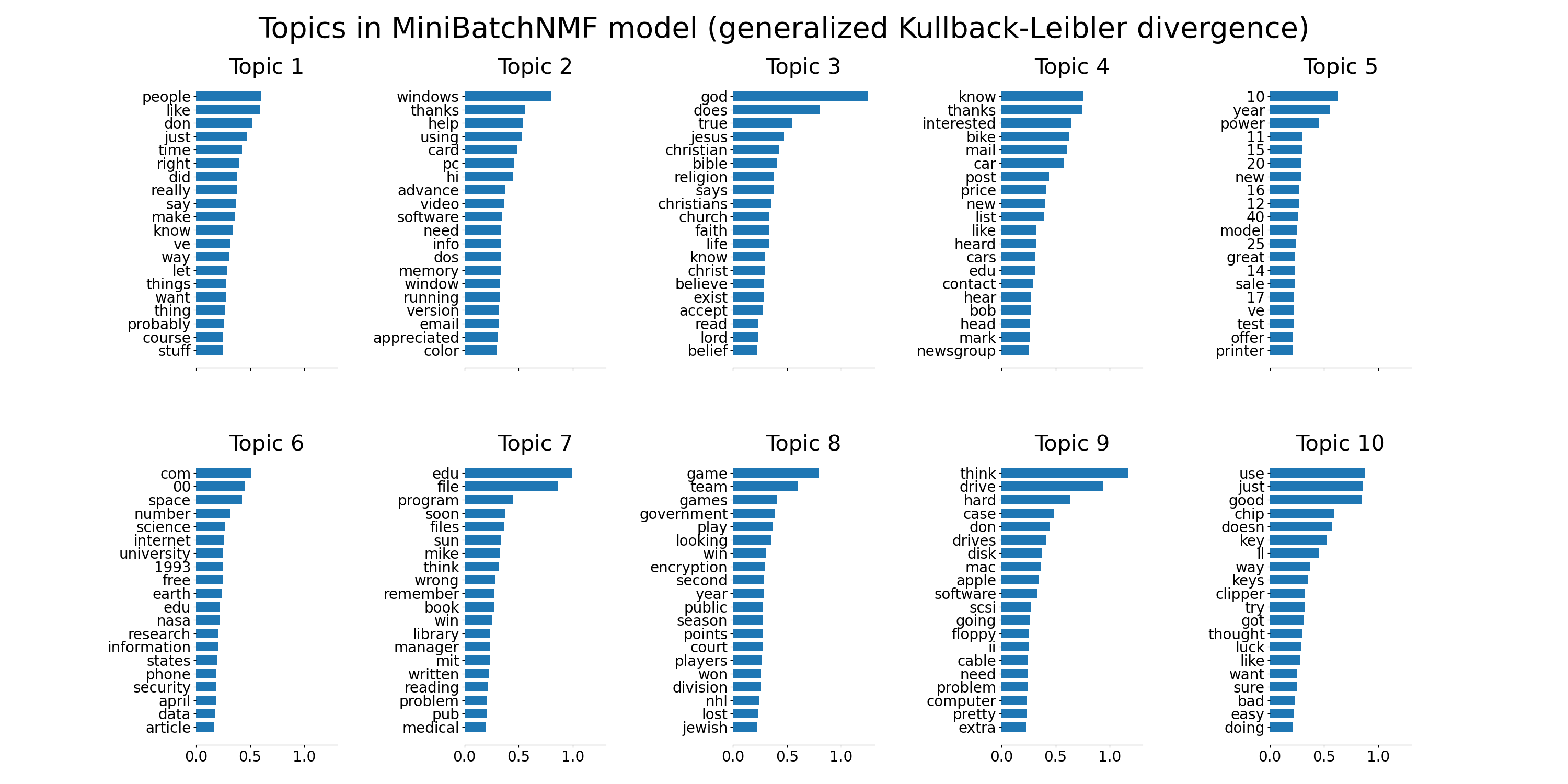
tfidf_feature_names = tfidf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
plot_top_words(
mbnmf,
tfidf_feature_names,
n_top_words,
"Topics in MiniBatchNMF model (generalized Kullback-Leibler divergence)",
)
print(
"\n" * 2,
"Fitting LDA models with tf features, n_samples=%d and n_features=%d..."
% (n_samples, n_features),
)
lda = LatentDirichletAllocation(
n_components=n_components,
max_iter=5,
learning_method="online",
learning_offset=50.0,
random_state=0,
)
t0 = time()
lda.fit(tf)
print("done in %0.3fs." % (time() - t0))
tf_feature_names = tf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
plot_top_words(lda, tf_feature_names, n_top_words, "Topics in LDA model")
Gesamtlaufzeit des Skripts: (0 Minuten 9,887 Sekunden)
Verwandte Beispiele
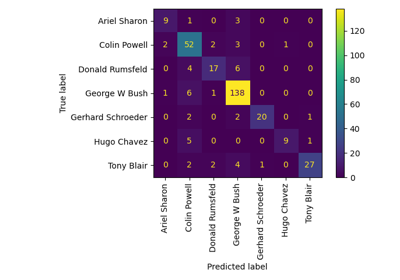
Gesichtserkennungsbeispiel mit Eigenfaces und SVMs
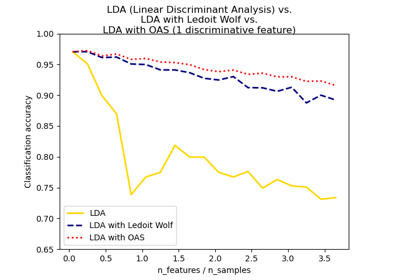
Normale, Ledoit-Wolf und OAS Lineare Diskriminanzanalyse zur Klassifikation